A Complete Guide to Ergonomics and Senior Safety

Ergonomics is the science of identifying the correlation between humans and the systems, and optimizing the system for humans to make it easier to use. The primary goal of ergonomics is to make workplaces safer and more comfortable. However, ergonomics plays a critical role in senior care too.
Let’s learn about how senior care and ergonomics are related.
Ergonomics and Senior Citizens
Contrary to popular belief, ergonomics is not limited to correcting seating at workplaces. With this science, you can learn about the physical abilities and limitations of the human body. It can help you make the environment safer for people, whether at work or home.
As ergonomics considers an individual’s strength, sensory abilities, and other physical limitations when designing a system or place, it can play a vital role in making living easier and safer for elders. Unfortunately, most people still fail to realize the importance of ergonomics for seniors.
While ergonomics tries to prevent the risk of developing chronic pain or injury among adults, it can help alleviate the pain resulting from existing chronic physical conditions in the case of seniors.
Whether it is reduced co-ordination or impaired vision, senior-friendly ergonomics can help elders use home appliances or move around in the house. For example, an ergonomically designed chair can help seniors alleviate back pain or avoid the risk of pulling a muscle.
Senior ergonomics is fast becoming a necessity as the number of seniors is growing. According to United States data, one in six people in the world will be over age 65 (16%) by 2050, up from one in 11 in 2019 (9%). By the same time, one in four persons living in Europe and Northern America could be aged 65 or over.
How Ergonomics Works/ Types of Ergonomics
As ergonomics involves studying how individuals interact with objects in their environment, it works in tandem with several other branches of science, including engineering, physiology, medicine, and psychology.
When it comes to senior ergonomics, you have the following three primary disciplines:
1. Physical
Physical ergonomics is the science of identifying how the human body responds to the surrounding environment while performing various activities. It may include using appliances or taking care of household chores. So, it covers biomechanics, which involves studying various body movements, physiology of your body like the state of your muscles and bones, and anthropometry, which concerns human body measurements and proportions.
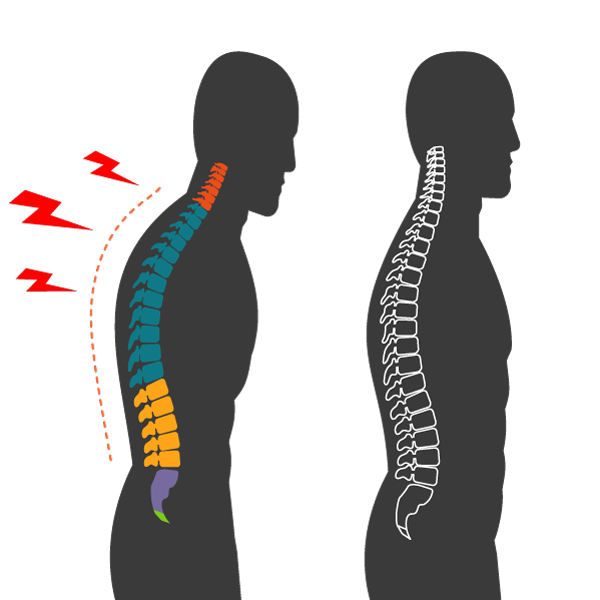
2. Organizational
The organizational element of ergonomics takes into account communication, daily schedule of the individual, movement in the house or workplace, and managing resources. It essentially combines the various elements of physical and cognitive ergonomics to create a safer and comfortable work environment.

3. Cognitive
This element of ergonomics focuses on establishing the co-relation between a product or system and the individual’s cognitive abilities such as perception, mental processing, and memory. Several psychological factors such as mental stress, productivity, concentration, and decision-making are a part of cognitive ergonomics.
Home Ergonomics for Seniors
Each year one out of every four Americans aged above 65 suffers a fall, which is the leading cause of fatal injury and the most common cause of nonfatal trauma-related hospital admissions among older adults.
While there are many reasons behind slips-and-falls among the elderly, cluttered households and things like broken steps are one of them. That’s why having an ergonomically-designed home can help prevent slips-and-falls to a great extent.
Depending on the physical abilities and health concerns, you may need to incorporate a few special ergonomic arrangements. However, in most cases, taking a few general steps can make the house more comfortable and safer for the elderly.
1. Living Room
Living room may not be the most commonly used room. However, this is where the elders will enter and exit the house, and entertain guests. So, it needs to be organized properly.
- Seating: Seating needs to be easily accessible and comfortable. Pay attention to the layout of the room. For example, sofa or an armchair should be at a comfortable distance and angle. Sofas and chairs should also have high backs with enough lumbar support.
- Lighting: The room should be well-lit. Elders have a shorter reach than adults. So, place the switches at an accessible height.
- Floor: Make sure to keep the floor clutter-free. Avoid using carpets if possible. If you must use them, have them fixed to the floor. You should also avoid door steps and uneven flooring. If there are steps, make sure they are even. Be sure to keep the floor dry and clutter-free at all times.
- Furniture: Place furniture at a comfortable distance as it allows your loved ones to walk easily. Make sure it doesn’t have sharp edges. It should also not be unstable, be it sofa, chairs, or cupboards.
- Appliances: The three most common appliances you can find in a living room are TV, phone, and a music system. Make sure they are easily accessible. TV should be placed at a comfortable viewing angle.

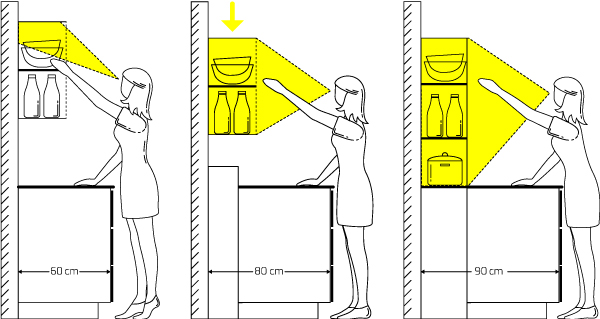
2. Kitchen
The kitchen is a very busy room in most homes. It is also the place where most of the action takes place. So, it needs to be safe and comfortable.
- Lighting: It should be well-lit, especially the table, stove, and workbenches. Make sure the switches are no more than a meter or meter-and-a-half above the ground level.
- Space: Keep the layout as clutter-free and as accessible as possible. A minimalist kitchen would be the best fit in most cases. People should be able to move easily and comfortably in the kitchen.
- Appliances: Avoid putting the refrigerator next to the stove. All the appliances should have frontal knobs, placed at comfortable height (better reach), bold instructions (vision impairment), and loud signals (hearing loss).
- Shelf Height: Install the shelves at the right height. For cabinets with doors, make sure there is enough room to move wheelchairs and legs. Your loved one shouldn’t have to kneel, stoop, stretch, or reach for anything.
- Furniture: Elders shouldn’t have to step on stools or chairs at all. Avoid using furniture with sharp edges. Place less accessed objects on the upper shelf and the rest at a comfortable height.
- Floor: Floor should be even, dry, and without any carpeting. Carpets are fire and tripping hazards in a kitchen.
3. Home Office
If your loved one has a home office, you will need to take a few ergonomic precautions, especially if they are using a computer.
- Chair: Make sure to use a chair that supports the correct body posture and offers excellent lumbar support.
- Proper Sitting Posture: Adjust the height such that your feet touch the floor, and your knees bend at a 90-degree angle.
- Screen Setup: Set the computer screen at the viewer’s eye level. It will help avoid neck fatigue.
- Keyboard: Using a keyboard and mouse for long hours can put a lot of stress on your wrists and hands. You can use padded wrist rests for the keyboard and mouse to ease the wrist pain.
- Footrest: For elders with shorter height, you need to use an adjustable chair and a table with a footrest.
- Key Objects: You can also use other ergonomic tools such as computer screen filters to avoid eye strain, and use typing stands to avoid putting a strain on your neck.

4. Bathroom
The bathroom is one of the most common areas where elders are likely to fall as it can be wet and slippery. Senior ergonomics can play a crucial role in keeping elders safe here.
- Lighting: Plenty of natural and artificial light is a must with easily accessible switches.
- Floor: Use a no-skid carpet on the floor, especially near the shower and bathtub. The floor should be even, around the doors. Make sure there is plenty of free space for elders in wheel chair to move around.
- Cabinets: Use safety lockers for drawers. Install cabinets at the right height and position to ensure easy access. There should be enough free space to move around after opening shelves and cabinet doors.
- Bathroom Accessories: You need support bars and stools in the shower, near bathtub, basin, and toilet. They should be comfortable to hold and offer a firm grip. The shower box should have a sliding door with a minimum width of 90 cm. Keep all the toiletries easily accessible. Water taps should also be easily accessible.

5. Bedroom
The bedroom needs to as comfortable and safe as possible because this is where your loved one will relax and sleep.
- Bed: Make sure to use a plush mattress and place it at the knee-high level for easy access. Having moveable railings on either side of the bed can prevent falls during sleep.
- Furniture: Set up a knee-high bench at the foot of the bed for dressing. You can also use a motorized recliner as an additional seating arrangement. You can also use a bed-top table for having breakfast, lunch, and dinner in bed for elders with mobility restrictions. A footstool is essential if your loved one’s feet tend to swell often.
- Lighting: Use easily accessible switches to ensure the room is always brightly lit. Any electrical equipment should be accessible from the bed.
- Floor: The carpeting should be fixed to the floor. Keep the floor clutter-free at all times. The floor plan should consider the room to move around in a wheelchair.
- Wardrobe: It should be well-lit. Make sure the partition is not too high. You can use a pull-down wardrobe lift if the rods are too high. There should be enough room to move around in a wheelchair.

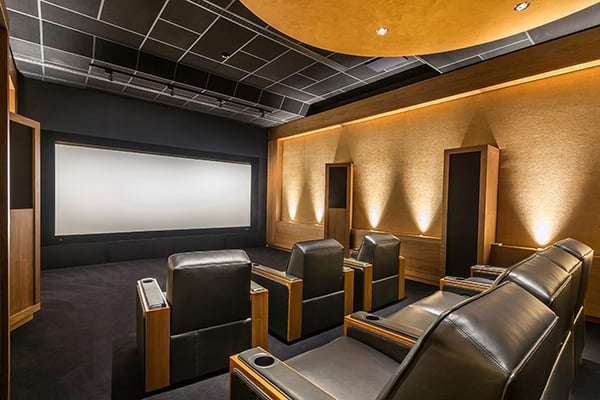
6. Home Theater
Entertainment is a necessity for most elderly, especially if they are living alone. It helps them connect with the rest of the world. If your loved one has a home theater, take the following ergonomic precautions.
- Floor: It should be even, if possible. For instance, you can use even floor if there is only one line of recliners. For multiple rows, consider installing a riser with a ramp.
- Lighting: When you are not watching movies, the lighting should be bright. Switches should be accessible. Floor should be marked with glowing markers to show directions.
- Seating: Your best bet is using ergonomically designed home theater seating. When choosing home theater recliners, consider the ones designed with human height, weight, and proportions in mind. They should offer excellent lower lumbar and head support when watching the big screen. The seating should allow your loved one to watch movies without any stress or fatigue.
- Space: When designing the layout, make sure there is enough room to move around in a wheelchair.

Ergonomics for Some of the Most Common Old Age Health Problems
While general ergonomic precautions can help you create a safer and more comfortable living environment, it may not be suitable for everyone. Sometimes, depending on a specific ailment or medical condition, you may need to take special precautions. Here are a few common old age problems and ergonomic solutions for them.
1. Spine Issues
Causes: Common spine-related problems in older adults occur due to degenerative discs, spinal stenosis, and osteoporosis.
Symptoms: Degenerative discs can lead to stiffness and intermittent pain, while spinal stenosis can cause lower back pain and numbness and weakness in legs. Osteoporosis can lead to frequent fractures.
Ergonomics Advice: Your loved one should use a chair with a backrest that offers excellent lower back support. When working on a computer or watching a TV, make sure to place the screen at the viewer’s eye level. Always sit up straight or adjust the armrest and the backrest of a chair accordingly.

2. Arthritis
Causes: Arthritis starts to set in as the cartilage tissue begins to weather away, mostly due to old age. However, Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), a type of arthritis, is an autoimmune disease.
Symptoms: Arthritis causes pain in all the joints, especially when moving. The pain can be low and intermittent or severe and long-lasting, even when the person is resting.
Ergonomics Advice: You can use a variety of ergonomic tools and devices, including pens, cutlery, chairs, support bars, furniture, and kitchen appliances, to help comfort your loved ones suffering from arthritis. For example, an ergonomically designed scoop plate and the scooper bowl can help your loved one dine with ease. The curved side allows one to easily scoop up food.
3. Muscle Strain
Causes: Muscle strain, also called pulled muscle, is a fairly common health condition among elders. A fall, overexertion, and sudden movement can cause muscle strain.
Symptoms: The most common symptoms are muscle spasms, swelling of the affected area, recurring or continuous pain, numbness and stiffness of the affected area, and difficulty in moving the injured muscle.
Ergonomics Advice: You can avoid potential muscle strain by taking ergonomic precautions. Using an ergonomically designed work desk, kitchen table, bathroom, seating arrangement, and furniture can help you avoid sudden movement, and the pulled muscle resulting from it.
4. Knee Pain
Causes: Many chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis, arthritis, gout, physical trauma, accident, or torn ligaments are among the common causes of knee pain.
Symptoms: The most common symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and even bone spurs. The pain will also make it hard for your loved one to move, putting a lot of restrictions on their mobility.
Ergonomics Advice: The knee is the biggest joint in the human body which also bears its weight when we move. So, keeping it in top shape is extremely necessary. Use an ergonomically designed chair if you are going to sit for long hours, be it in your bedroom or home office or TV room. The chair should offer proper lumbar support and your legs should touch the floor or footrest comfortably.

5. Neck Pain
Causes: Prolonged poor posture is perhaps the most common cause of neck pain. However, injury from a fall, contact sports, or whiplash can also lead to injury pain.
Symptoms: The most common symptoms are pain and stiffness. Sometimes, you may also experience swelling or numbness.
Ergonomics Advice: When you are working on a computer or watching a TV, it is necessary to maintain the right posture to avoid neck pain. Use an ergonomically designed height-adjustable chair when working on a computer. Keep the screen at eye level and about an arm’s length away. When watching TV or a home theater screen, use a comfortable recliner with right lumbar support and viewing angle to avoid neck pain.
6. Shoulder Pain
Causes: Shoulder pain can arise from excessive stress or incorrect posture. It may also be caused by overuse, disuse, sprain, strain, or sleeping on one side, in case of seniors.
Symptoms: Shoulder pain often develops gradually. So, identifying early symptoms is a tough task. Your loved one may experience recurring pain when sleeping or sitting. The pain can eventually lead to stiffness and numbness.
Ergonomics Advice: Ergonomics can help alleviate existing shoulder pain and preventing it from developing further. When setting up a home office for your loved one, remember the 90-degree rule. Use chairs designed to keep your head and torso stationary.
7. Wrist Pain
Causes: Arthritis can be one of the primary causes of wrist pain in the elderly. Prolonged use of computer can also result in wrist pain.
Symptoms: The most common symptoms are stiffness, numbness, swelling, and also continuous pain.
Ergonomics Advice: If your loved one uses a computer, you should provide them with wrist pads to prevent wrist strain. Keeping things like light switches, cutlery, clothes, and other items within their reach can also help prevent pulling or spraining their wrist muscles. Make sure to use lightweight stools and chairs to avoid wrist injuries. Using arthritis-friendly cutlery can also help you avoid wrist injuries.

Ergonomics for Hobbies
Most senior citizens have one hobby or another. So, you need to consider ergonomics that your loved one can follow when pursuing their hobby. These ergonomic precautions are not necessarily about using tools, but also about maintaining a correct posture for the desired task.
1. Gardening
Whether it is kneeling or leaning over, gardening often involves staying in different awkward positions for a considerable time. So, for most seniors with severe medical conditions, such as arthritis, gardening can be a challenging hobby to pursue. As a result, taking ergonomic precautions is more necessary than ever if your loved one is into this activity.
Keep the following things in mind:
- Take frequent breaks to avoid overexertion and fatigue. Don’t extend your arms or legs for more than 10-15 seconds.
- Avoid lifting rake leaves or any other trash. Instead, collect them on a tarp and pull it to the garbage can or compost pit.
- Avoid using thick gloves as they may weaken your grip, increasing the chances of an accident.
- Try to avoid awkward or strenuous postures whenever possible. Always keep your elbows below heart level.
- Avoid repetitive movements such as bending or pulling to avoid stressing out your muscles and joints.
- Don’t wriggle your wrists too much when working. Keep your wrists in a neutral position as for as possible.
- You can use tools with telescopic and pistol grip handles as they require less gripping strength. Also, use ergonomic garden tools if you can.
- Label all your tools in bold letters for easy identification.
- Don’t go out of your comfort zone when working in your garden. Keep everything within your arm’s reach.

2. Sewing and Knitting
As kids, almost all of us have seen our grannies knitting a Christmas sweater. Most elderly women spend time sewing, quilting, and knitting. However, this hobby can lead to a few posture-related problems if proper care isn’t taken.
- Always work in a well-lit area to avoid straining your eyes. If you wear glasses, keep them on when you are working.
- Take frequent breaks as all these activities involve repetitive motions. A break every 15-20 minutes should be excellent.
- Good posture is the bedrock of sewing and knitting. Choose a comfortable chair that will help keep your back straight, arms by the sides, and allow you to look up when working.
- The armrests shouldn’t be too high or too low. The height should be such that you shouldn’t have to raise your shoulders or extend your elbows too much.
- Avoid twisting your hips, back, or neck. You can use an ergonomic seat cushion to adjust your posture correctly when knitting.
- You can also use ergonomically designed sewing tables that will help you reduce hunching.
- If you are going to do any of these activities while standing up, make sure to use shoes and floor mats designed to prevent your legs from feeling tired or sore.
- You should also consider buying ergonomic knitting and sewing tools as they can offer a better grip without straining your muscles or joints.
- Keep your wrists straight when using needles, scissors, and other tools.
- Your work-station should be at elbow height.
- Keep everything you need within your reach. You don’t want to extend your limbs too much to pick something up as it could lead to a sprain or pulled muscle.
- If you experience any pain, soreness, dizziness, tingling, or numbness in any body part, stop your work immediately. Find out why you were feeling uncomfortable and take the necessary steps to alleviate your pain. If the discomfort persists, call your doctor promptly.

3. Music
If your loved one plays musical instruments, you need to take a few ergonomic precautions as it often involves repetitive movements.
- Make sure to use a chair or stool or bench that helps you maintain the right posture when playing an instrument, if you are seated. When sitting down, make sure your hips and knees are at the same level.
- When playing keyboard instruments such as piano, make sure to use an ergonomically designed stool or chair to adjust your height and posture.
- You can buy ergonomic string instruments that are light, help reduce pressure on joints, and relieve neck and shoulder fatigue.
- You can also find ergonomically modified brass instruments. For example, fiberglass mouthpieces can help you play in cold weather.
- Regardless of the instrument you play, make sure to keep everything within your arm’s reach.

4. Book Reading
Reading is perhaps the most comfortable and least expensive hobby for the elderly. However, it also demands a few ergonomic considerations.
- If you have a reading chair, make sure your knees form a perfect 90-degree angle, and your feet touch the floor comfortably.
- The edge of your chair shouldn’t stop blood circulation to your legs.
- You can use a cushion or footrest to adjust your body posture.
- Read in a well-lit room. It should help avoid eye fatigue.
- Excellent lumbar support is most essential part when reading because hunching can certainly lead to back and neck pain.
- You must also keep your spine in a neutral position.
- Hold the book at eye-level. Use pillows to support your elbows, if necessary. You can also use an ergonomic book reading stand.
- Finally, make sure to take frequent breaks. It will help avoid numbness resulting from sitting in one posture for long.

Benefits of Ergonomics
Taking all these ergonomic precautions can help your loved one live a better life, if not eliminate their physical ailments.
- Ease of Use: Chronic conditions like arthritis make it challenging for many elders to use cutlery, appliances, and instruments. Ergonomics, on the other hand, offers ease-of-use for people suffering from these conditions.
- Comfort: The ease-of-use, in turn, helps increase the level of comfort for the elderly by alleviating any pain caused by existing medical conditions. Increased comfort means your loved ones can live a happy and engaging life on their own.
- Safety: It also provides your loved ones with a safer living environment. It can help reduce accidents such as slip-and-fall.

Parting Words
As you can see, ergonomics is not merely limited to the workplace. Elders living alone or in the care of someone can also benefit significantly from ergonomic practices, instruments, and tools. From home theater seating to the kitchen, you can incorporate ergonomics into almost every facet of your loved ones’ lives. Hopefully, this detailed guide will help you understand how senior ergonomics works and how your loved ones can benefit from it. Feel free to take this discussion forward, and talk about senior ergonomics in the comments section below.

